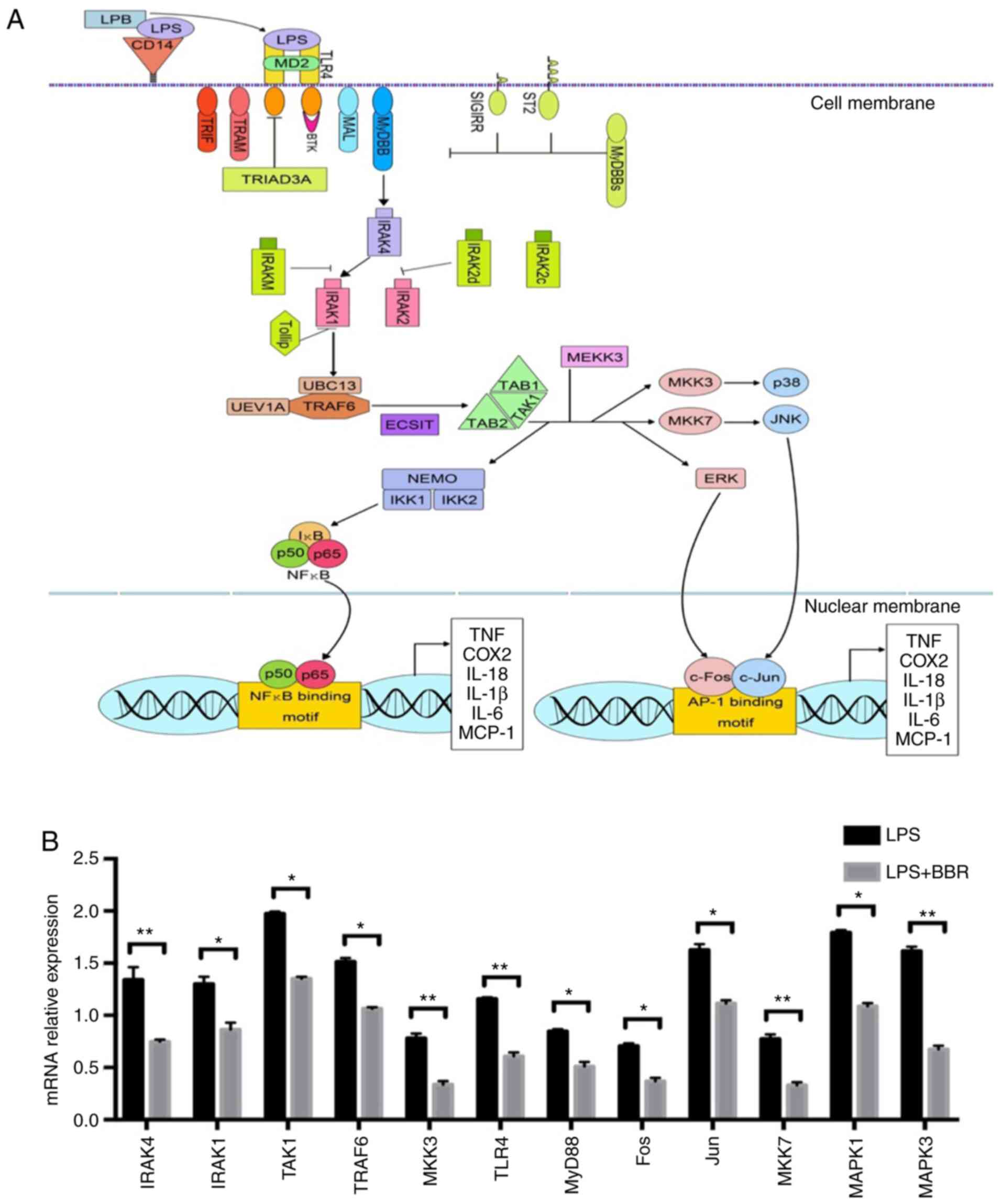
Eriocitrin in combination with resveratrol ameliorates LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells and relieves TPA-induced mouse ear edema - ScienceDirect

Inhibitory Effect of Jing-Fang Powder n-Butanol Extract and Its Isolated Fraction D on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in RAW264.7 Cells | Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics

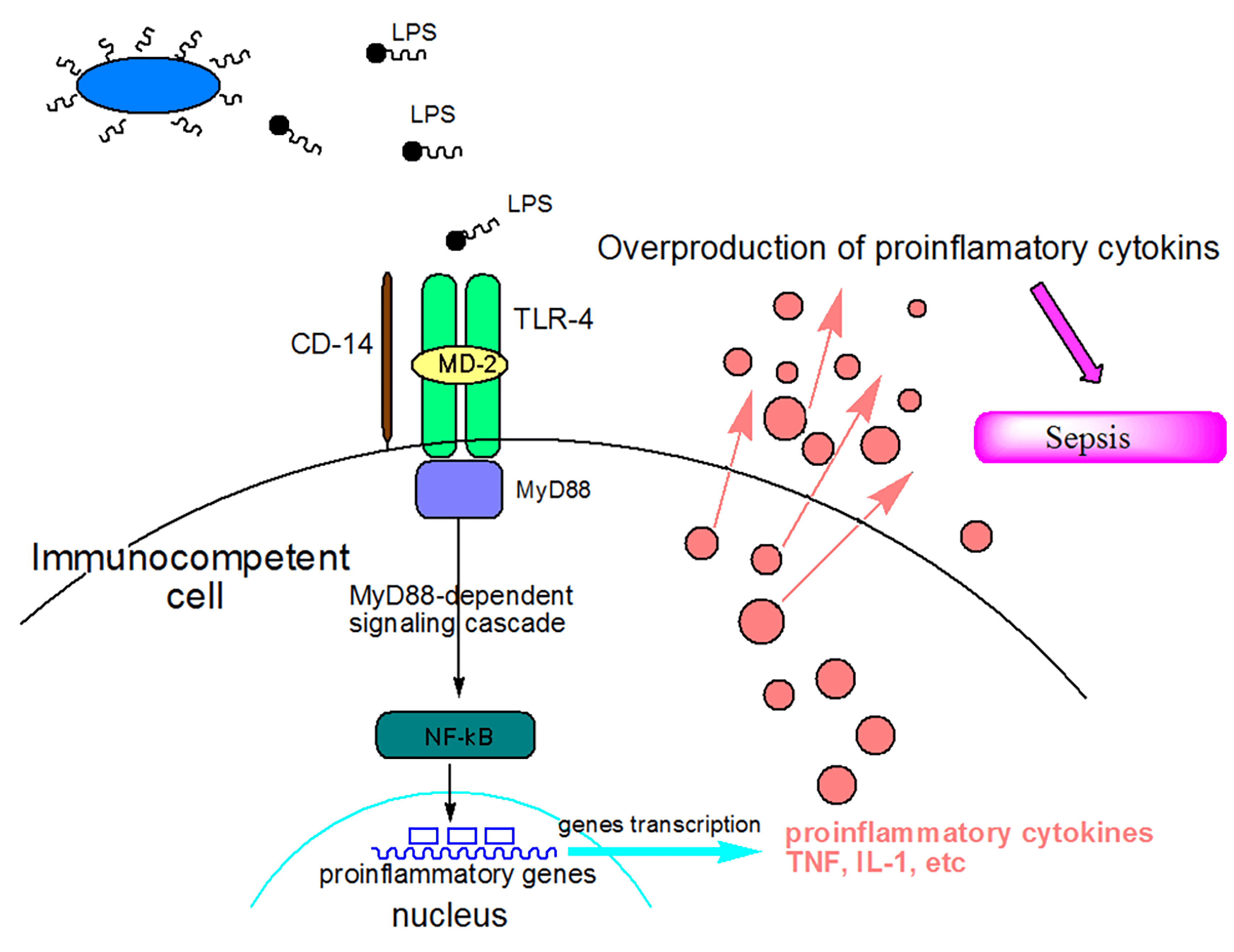
Proposed model of LPS-induced systemic inflammation that results in BBB... | Download Scientific Diagram

Directly interact with Keap1 and LPS is involved in the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of (-)-epicatechin-3-gallate in LPS-induced macrophages and endotoxemia - ScienceDirect
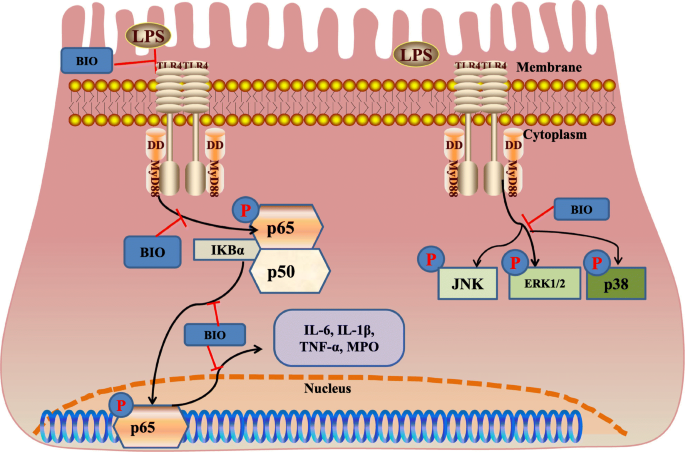
6-Bromoindirubin-3′-Oxime Suppresses LPS-Induced Inflammation via Inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB and TLR4/MAPK Signaling Pathways | SpringerLink
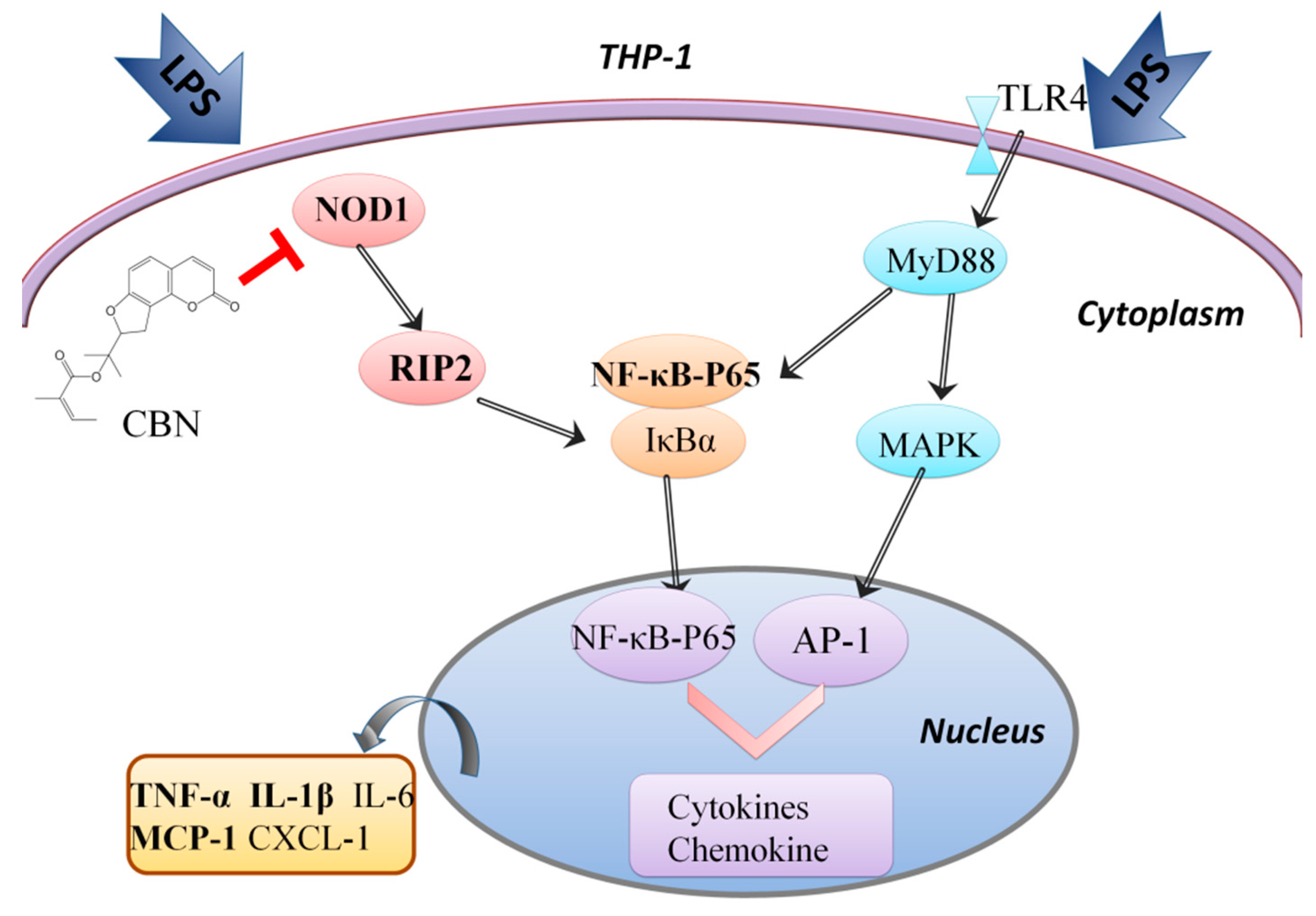
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Columbianadin Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide ( LPS)-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis through the NOD1 Pathway | HTML

Desoxyrhapontigenin, a potent anti-inflammatory phytochemical, inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory responses via suppressing NF-κB and MAPK pathways in RAW 264.7 cells - ScienceDirect

2′-Hydroxy-5′-methoxyacetophenone attenuates the inflammatory response in LPS-induced BV-2 and RAW264.7 cells via NF-κB signaling pathway - ScienceDirect
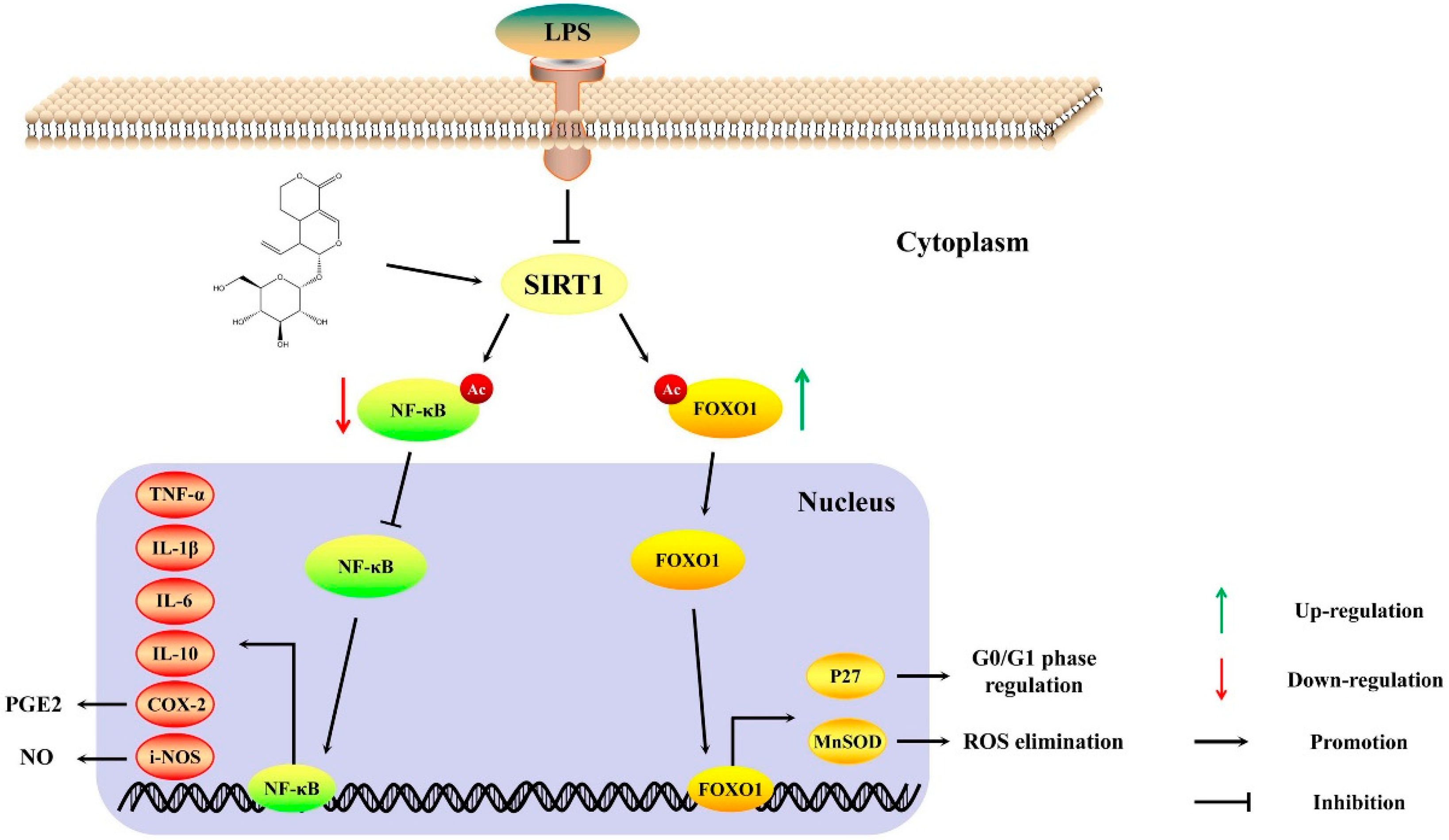
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Sweroside Alleviated LPS-Induced Inflammation via SIRT1 Mediating NF-κB and FOXO1 Signaling Pathways in RAW264.7 Cells

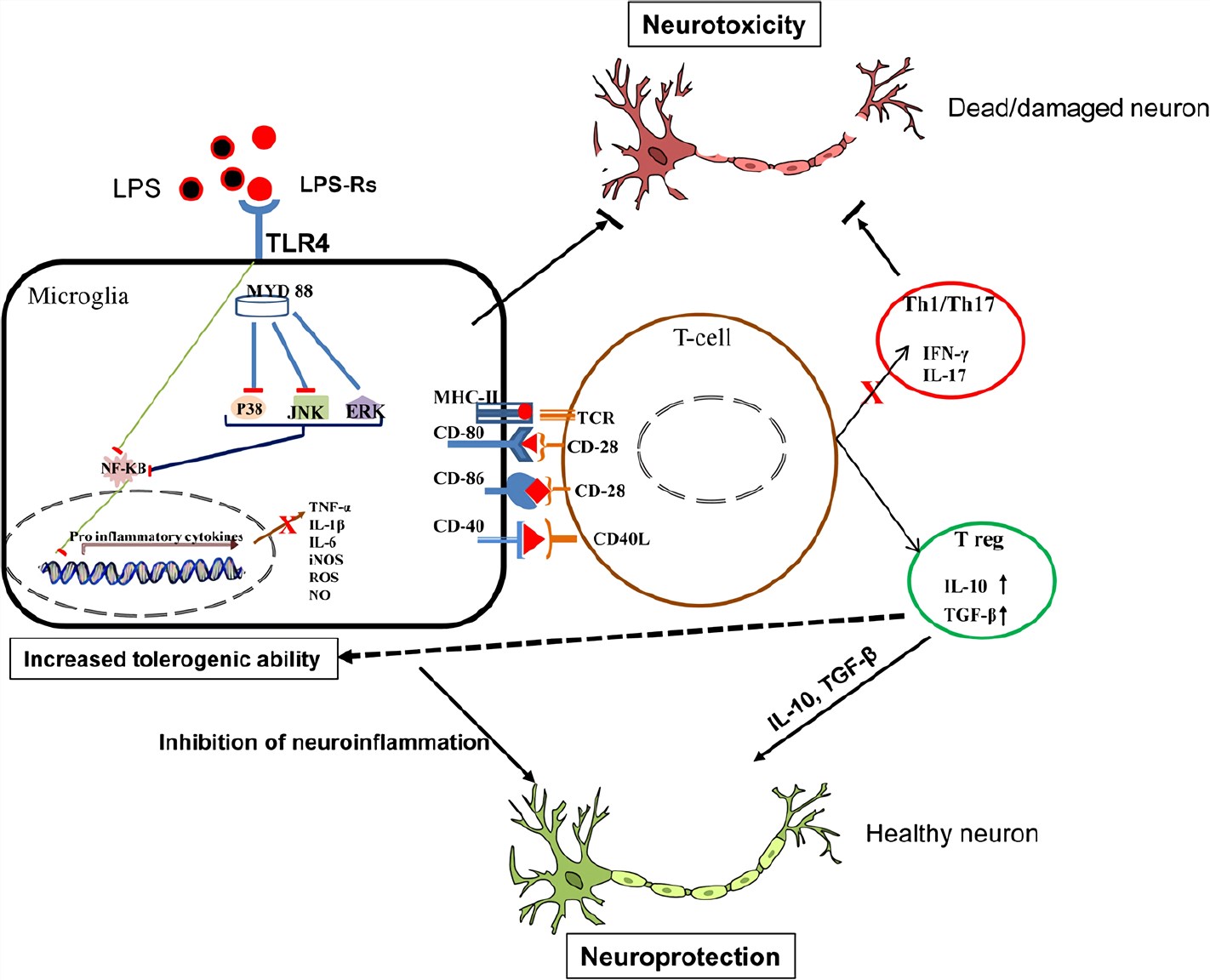
Signaling mechanisms of growth hormone-releasing hormone receptor in LPS- induced acute ocular inflammation | PNAS

Amelioration of 4-methylguaiacol on LPS-induced inflammation in THP-1 cells through NF-κB/IκBα/AP-1 and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway - ScienceDirect
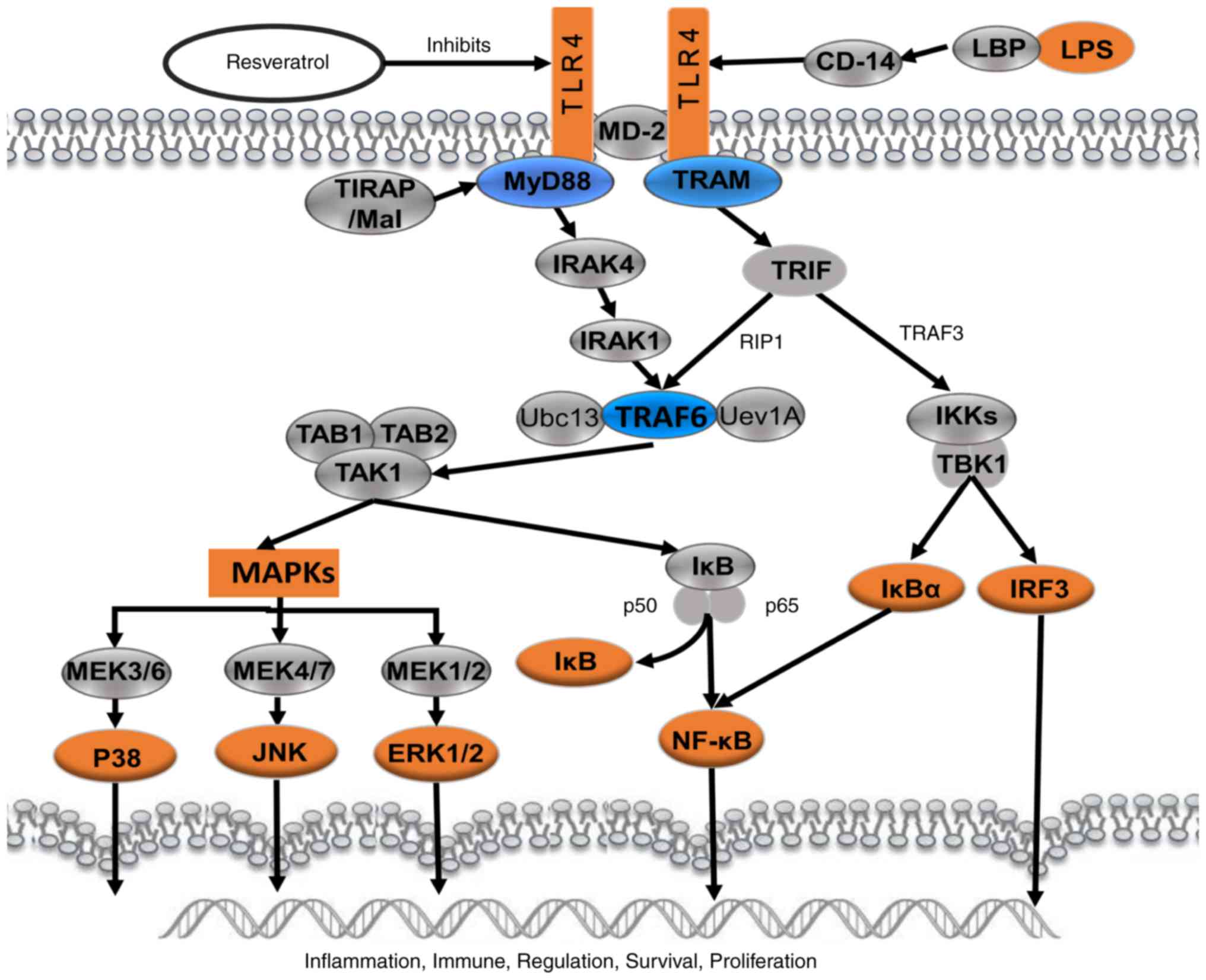
Resveratrol inhibits LPS‑induced inflammation through suppressing the signaling cascades of TLR4‑NF‑κB/MAPKs/IRF3
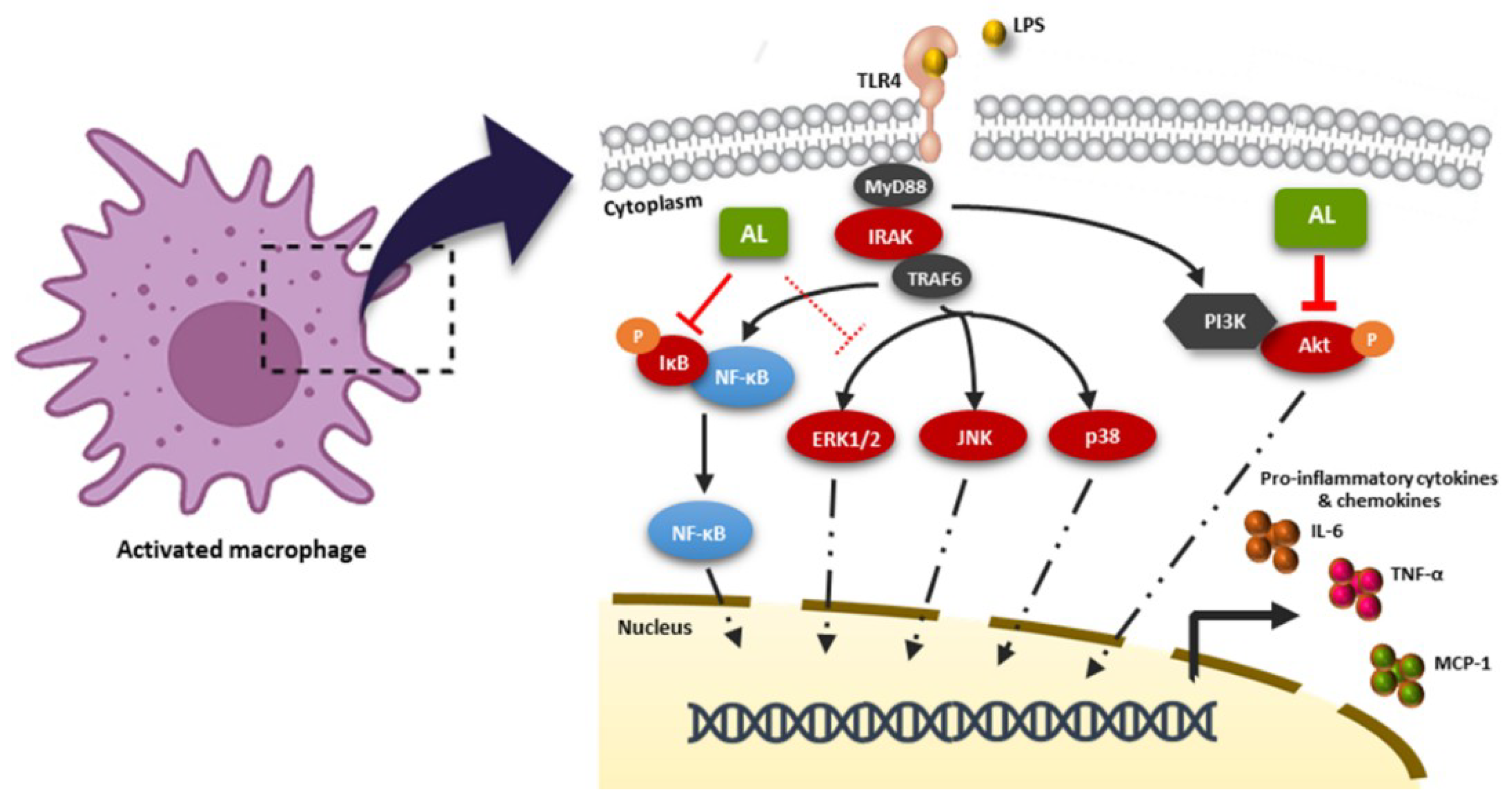
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Artocarpus lakoocha Extract Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response in RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells
The Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Mechanisms of Eupafolin in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses in RAW264.7 Macrophages
PLOS ONE: 4'-Hydroxywogonin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 macrophages and acute lung injury mice
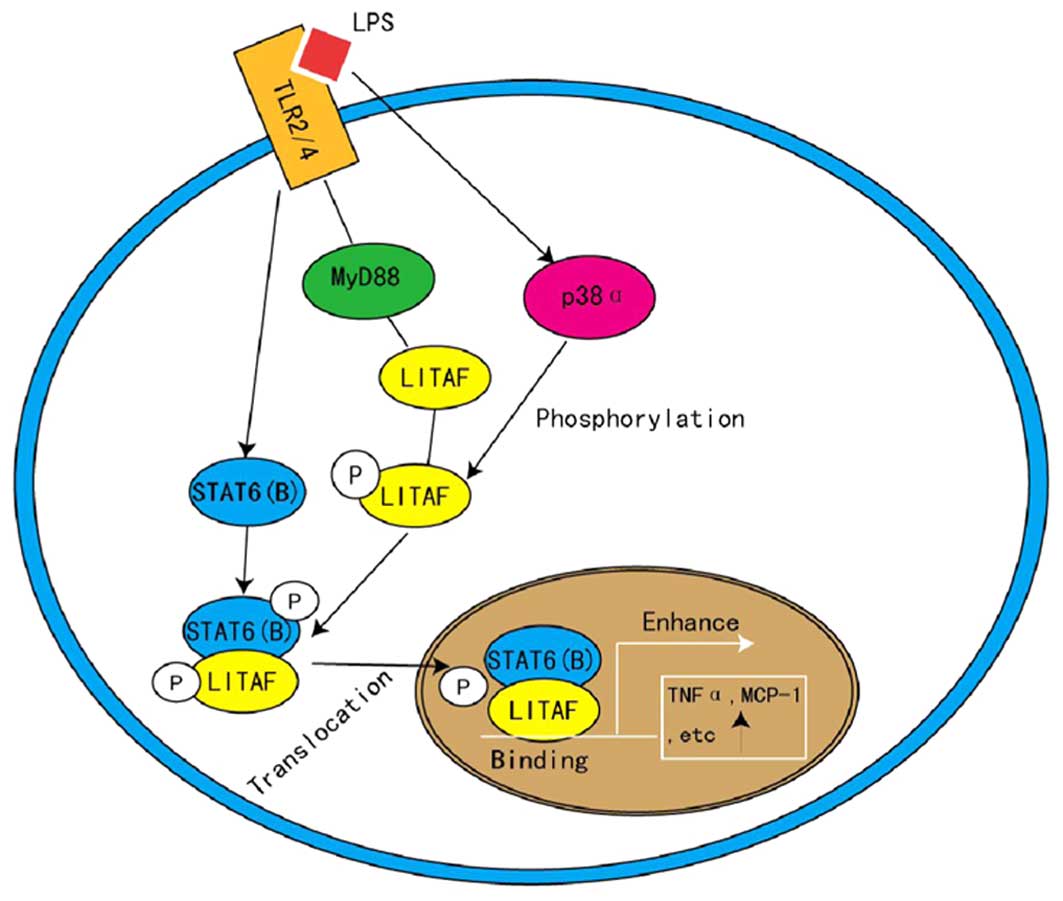
Lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-α factor enhances inflammation and is associated with cancer (Review)
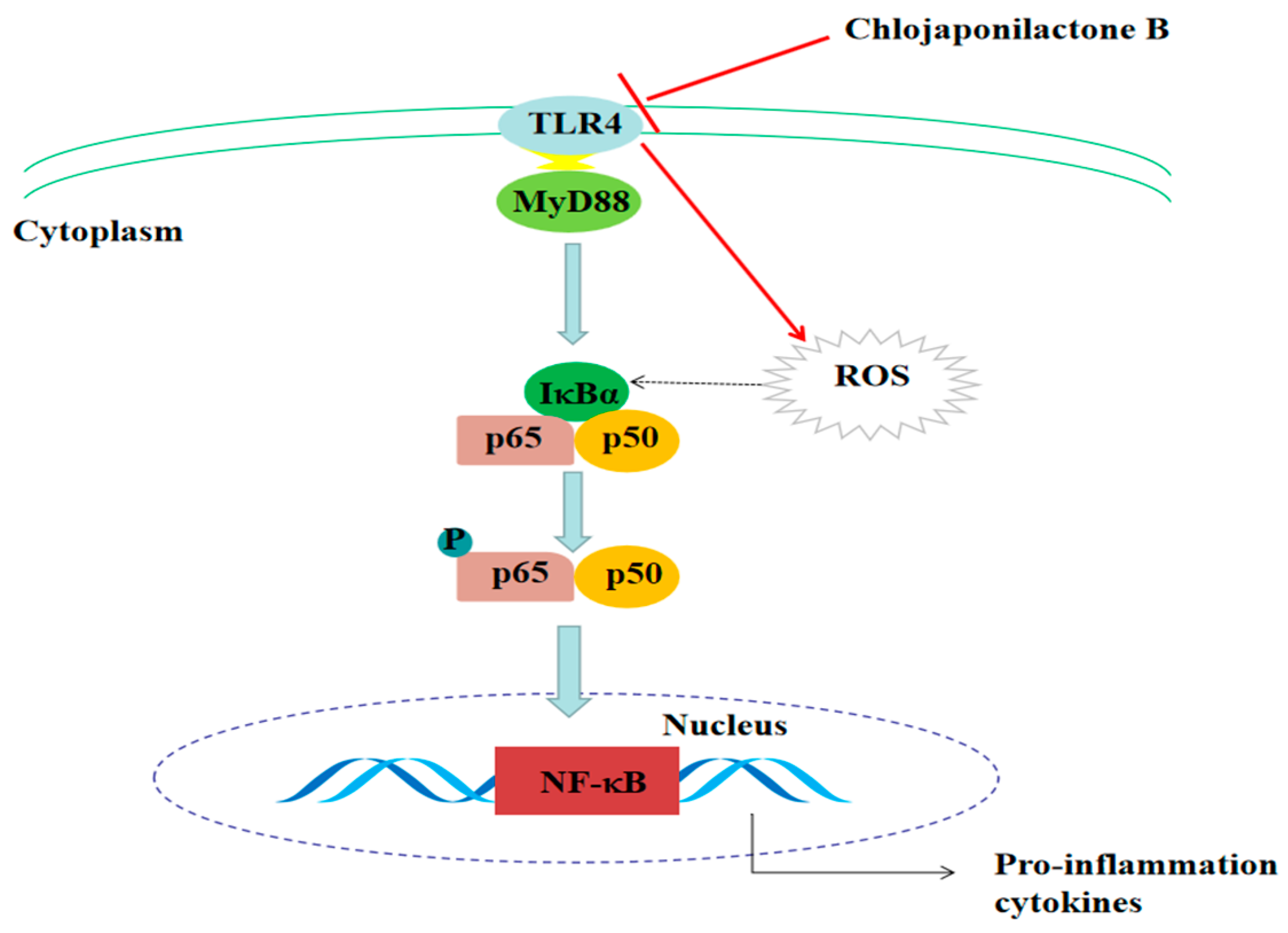
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Chlojaponilactone B Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses by Suppressing TLR4-Mediated ROS Generation and NF-κB Signaling Pathway | HTML